How to use WebServices with the Compact Framework
on PocketPC using HTTP/1.1 Compression
lire la version francophone 
In his tutorial Retrieving
Data from Web Services using Standard HTTP 1.1 Compression,
Jacek Chmiel explains how to override the methods GetWebRequest
and GetWebResponse .NET Web Service's proxy class to
request the server data compression and uncompress them before
the SOAP envelop is parsed.
Though this approach is interresting, it
is unapplicable to the PocketPC because the Compact
Framework does not allow the overriding of these methods. But,
we realized that it is possible to define a new protocol, zhttp
for instance, that uses WebRequest and WebResponse
derived objects designed for compression.
And this approach works with the PocketPC!
 |
This article has been written with the Beta of the Compact Framework.
- To get the binaries for the zhttp version compatible with the Final Beta,
click here.
- To get the source files that uses the latest version of SharpZipLib, instead of the prior version NZipLib,
click here.
The implementation of ZHttpWebRequest of this version also override the WebRequest.Timeout property
and delegate the call to the underlying HttpWebRequest. Not doing this make any call to
the Timeout property throw a NotSupportedException.
|
Generalities
Apparently, the transfert sequence from a
SOAP call is :
- create an HTTP request through Webrequest.Create
with the http protocol;
-
prepare the request to send the SOAP envelop;
- wait for the response ;
- read the response stream to interpret
the results in the SOAP envelop.
Without changing anything to the WebServices
and SOAP objects, both client side and server side, the code we
developped create the following sequence :
- register the zhttp protocol;
- create an HTTP request through WebRequest.Create
with the http protocol ;
- create the internal HTTP request
through WebRequest.Create, without the "z"
- add the "Accept-Encoding:
gzip, deflate" header;
-
prepare the request to send the SOAP envelop;
- wait for the response ;
- waith for the internal
HttpWebrequest response;
- uncompress the response stram ;
- read the response stream to interpret
the results in the SOAP envelop.
Implementing ZHttpWebRequest
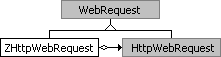 The
first step is to implement a class that handle the HTTP
request, adding the header that inform the server that the
client understands gzip or deflate answers. If
the server does not know either of these compression
algorithms, the data are sent uncompressed.
The
first step is to implement a class that handle the HTTP
request, adding the header that inform the server that the
client understands gzip or deflate answers. If
the server does not know either of these compression
algorithms, the data are sent uncompressed.
public class ZHttpWebRequest : System.Net.WebRequest
{
private HttpWebRequest request;
private System.Uri uri;
internal ZHttpWebRequest(System.Uri uri)
{
string s = uri.AbsoluteUri.Substring(1); // remove the leading z
this.uri = uri;
request = (HttpWebRequest)WebRequest.Create(s);
// tell the HTTP server that the client accept compressed data
request.Headers.Add("Accept-Encoding", "gzip, deflate");
}The next step consists in returning the ZHttpWebResponse
in the GetResponse
method, so that it can uncompress the data sent by the HTTP
server.
public override System.Net.WebResponse GetResponse()
{
ZHttpWebResponse response = null;
// create the appropriate response object
response = new ZHttpWebResponse(request, uri);
return response;
}Finally, all the others overloaded
methods should return the result of the internal HttpWebRequest
object.
// for all the other overridable functions, redirect the call
// to the private HttpRequest object, as shown above
public override void Abort()
{
request.Abort(); // redirect the call
}
...
}Implementing ZHttpWebResponse
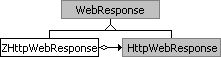 To
handle the response, the ZHttpWebResponse object
derives from WebResponse and retrieves the regular HttpResponse
object from the HTTP request object.
To
handle the response, the ZHttpWebResponse object
derives from WebResponse and retrieves the regular HttpResponse
object from the HTTP request object.
public class ZHttpWebResponse : WebResponse
{
private HttpWebResponse response;
private System.Uri uri;
internal ZHttpWebResponse(WebRequest request, System.Uri uri)
{
this.uri = uri;
response = (HttpWebResponse)request.GetResponse();
}The GetResponseStream method does
all the uncompressing job, whether the response is gzip
enconded, deflate encoded or not encoded at all.
public override Stream GetResponseStream()
{
// select the right decompression stream
if(response.ContentEncoding=="gzip")
{
return new GZipInputStream(response.GetResponseStream());
}
else if(response.ContentEncoding=="deflate")
{
return new InflaterInputStream(response.GetResponseStream());
}
else
{
return response.GetResponseStream();
}
}The next step is to override ResponseUri
to return the zhttp Uri. Then, all the others
overloaded methods should return the result of the internal HttpWebRequest
object.
public override System.Uri ResponseUri
{
get
{
return uri;
}
}
// for all the other overridable functions, redirect the call
// to the private HttpRequest object, as shown above
public override void Close()
{
response.Close();
}
...
}
Registering the zhttp protocol
The Web requests are handled through a class
factory that instanciate the WebRequest
objects able to handle the uri. So, http:// is
handled by HttpWebRequest,
file:// by FileWebRequest, etc.
The
following class, that implements IWebRequestCreate,
is used by the register function to instanciate the ZHttpWebRequest
objects.
class ZHttpWebRequestCreate : IWebRequestCreate
{
/// <summary>
/// Create the WebRequest object able to handle the Uri
/// </summary>
/// <param name="uri">the requested Uri</param>
/// <returns>The WebRequest object</returns>
public System.Net.WebRequest Create(System.Uri uri)
{
System.Net.WebRequest request = new ZHttpWebRequest(uri);
return request;
}
}Then, let the ZHttpProtocol class wrap
the call to the registration function.
public class ZHttpProtocol
{
/// <summary>
/// Register the protocol
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
static public bool Register()
{
return WebRequest.RegisterPrefix("zhttp",
new ZHttpWebRequestCreate());
}
}So now, to register the zhttp protocol,
we just have to call ZHttpProtocol.Register in our
code, before the first call to the web services, in the Main
function for instance.
// register the protocol
ZHttpProtocol.Register();
Changing the WebService's Uri
In order to use the zhttp protocol, the
Uri of the WebService objects must be changed by inserting a
"z" in front of the original Uri.
// initiliaze the WebService
MyWebService ws = new MyWebService();
ws.Url = "z" + ws.Url;
// call the methods
...
Et voilà !
Configuring IIS 5.0 Server to compress aspx and asmx files
Once the compression is activated for the
IIS 5.0 server, run the following commands to add the aspx and
asmx to the file types list the compression filter have to handle:
CSCRIPT.EXE ADSUTIL.VBS
SET W3Svc/Filters/Compression/GZIP/HcScriptFileExtensions
"dll" "asp" "aspx" "asmx"¶
¶
CSCRIPT.EXE ADSUTIL.VBS¶
SET W3Svc/Filters/Compression/DEFLATE/HcScriptFileExtensions
"dll" "asp" "aspx" "asmx"¶
¶
IISRESET.EXE¶
Some useful links...
Revision history...
| date |
révision |
| 01/26/2004 |
Source file update
Implementation of the property Headers at the line 374 to avoid
a NotSupportedException to be raised. (Thanks to Jeff Evans for reporting and correcting the bug). |
all the informations here are provided as is, without any warranty of any kind.
Copyright © FlowGroup SAS, 2002-2005



